Notice that p f is above the equilibrium price of p e.
Government set price floor on a product.
A price floor example.
Price floor is a price control typically set by the government that limits the minimum price a company is allows to charge for a product or service its aim is to increase companies interest in manufacturing the product and increase the overall supply in the market place.
Picture a competitive market with the usual upsloping supply curve and downsloping demand curve.
A price floor that is set above the equilibrium price creates a surplus.
Price ceilings and price floors.
Types of price controls.
Will attract more resources towards the production of the product.
Buffer stocks where government keep prices within a certain band.
However a price floor set at pf holds the price above e 0 and prevents it from falling.
If the current price is creating a shortage then market forces will cause the price to adjust and.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
Does not interfere with the rationing function of price in a market system.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
Will attract more resources towards the production of the product.
How price controls reallocate surplus.
Minimum prices prices can t be set lower but can be set above.
A government set price floor on a product.
Government price controls are situations where the government sets prices for particular goods and services.
The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied qs exceeds the quantity demanded qd.
This control may be higher or lower than the equilibrium price that the market determines for demand and supply.
Price controls are government mandated legal minimum or maximum prices set for specified goods.
This is the currently selected item.
Price and quantity controls.
Maximum price limit to how much prices can be raised e g.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
Figure 4 8 price floors in wheat markets shows the market for wheat.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
If the government agrees to purchase a specific maximum of unsold products at the price floor it.
Price floors can have differing effects depending on other government policies.
Percentage tax on hamburgers.
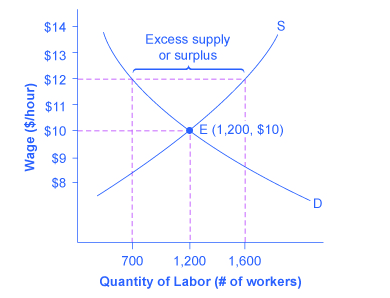
Minimum wage and price floors.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
Will drive resources away from the production of the product.
Limiting price increases in a privatised.
Suppose the government sets the price of wheat at p f.
The intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e 0.